Home Electrical Wiring
How electricity reaches your home ?
Complete DIY House Electrical Work
In this tutorial, we will discuss the first topic of how electricity reaches your home. This is the first topic of the tutorial series on basics of home electrical wiring specially designed for interior designers and architects.
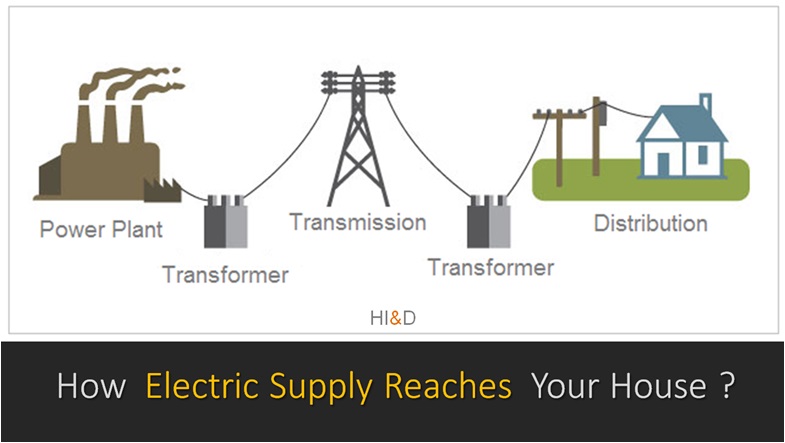
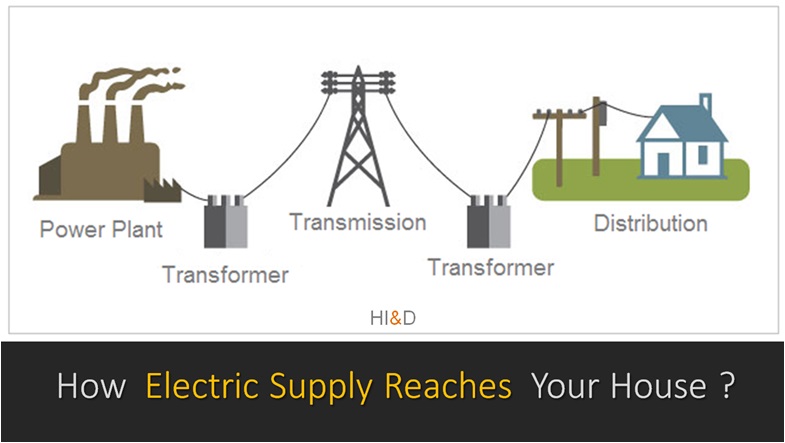
There are three major components of the entire electrical system. These three components are electricity generation, the second component is transmission and the third component is distribution.
This tutorial covers some basic information about how electricity supply reaches your home. Some key components include electricity generation, its transmission and finally its distribution to the end user.
Let us start with the first component that is electricity generation.
How electricity reaches your home ?
Electricity Generation
The electricity is generated in the electric power generation plants. The power plants use different types of fuel to generate the electricity.
The most common type of power plants includes hydroelectric power plants, nuclear power plants, and the thermal power plants.
After the electricity generation the next step is transmission.
Electricity Transmission
After its generation the next step is the electricity transmission to the destination city. The electricity produced is transmitted through a network of transmission lines , grid lines and distribution sub stations.
The electricity is transmitted with the help of network of huge transmission towers that carries electric overhead cables.
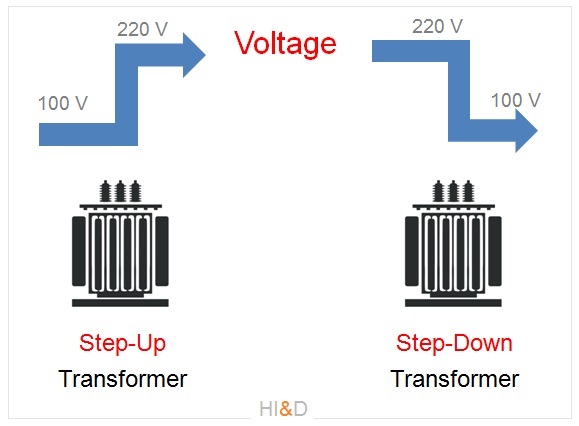
During its transmission the electric voltage is increased with the help of step-up transformers. The voltage increase during its transmission is done to compensate for the transmission losses.
The electric transmission and distribution network includes different categories of stations, control rooms and substations.
The electric supply transmission and distribution system is controlled and managed by the network of substations.
Electricity Distribution
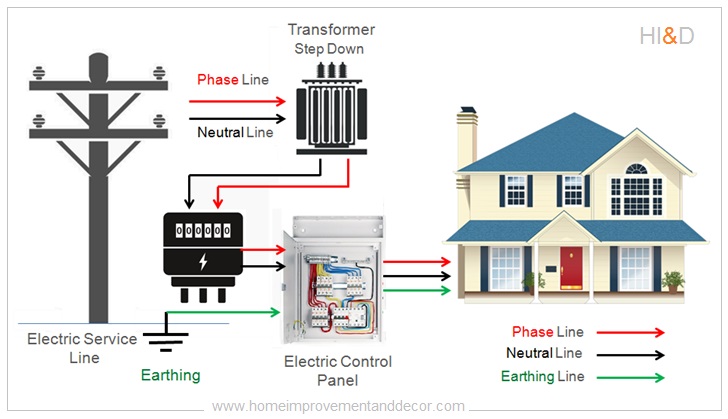
The electricity is supplied to various consumers either for the domestic consumption or for the industrial activity. At this stage, another type of electric transformers ( Step-down transformer ) is used to step-down the power transmission voltage as per the designated standard.
For residential purpose, depending upon the country specific electric supply standard, two types of power supply are commonly used. Most countries are having adopted to either AC 110 Volts at 60 Hertz Or AC 230 Volts at 50 Hertz.
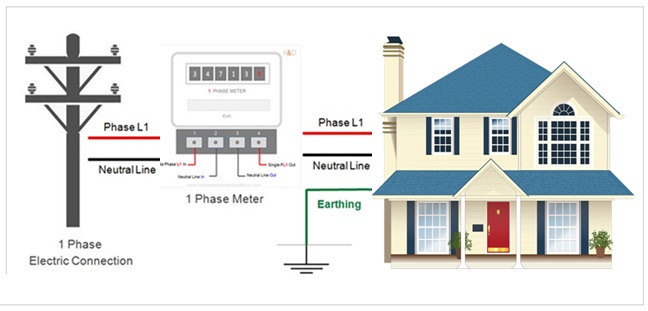
The electric power supply is given to your home either through overhead electric lines or underground cables. A step-down transformer is used regulate and supply the electricity to either single or multiple residential houses.
Depending upon the distribution system , electrical supply connection to the house either be connected directly to the outside electric service line or through a step down transformer placed inside the residential complex.
How electricity reaches your home ?
Electricity Distribution Standards
Country Wise Voltage
Each country has adopted a specific standard for the distribution of the electricity supply to the end consumer. The electricity is supplied to the to the consumer at specific voltage and frequency for residential use.
For example the US standard for residential purpose is distributed at 120 volts at 60 hertz. Whereas, in UK and India the electricity for the residential purpose is distributed at 230 volts at 50 hertz.
And for this reason, the electrical gadgets manufactured for the US market needs a special voltage regulator to work properly outside USA where the power supply standard is different.
Country | Voltage | Frequency |
Australia | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Brazil | 110 V | 60 Hz |
Canada | 120 V | 60 Hz |
China | 220 V | 50 Hz |
France | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Germany | 230 V | 50 Hz |
India | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Ireland | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Israel | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Italy | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Japan | 100 V | 50 / 60 Hz |
New Zealand | 230 V | 50 Hz |
Phillippines | 220 V | 50 Hz |
Russia | 220 V | 50 Hz |
South Africa | 220 V | 50 Hz |
Thailand | 220 V | 50 Hz |
United Kingdom | 230 V | 50 Hz |
USA | 120 V | 60 Hz |