Civil Engineering Terminology
Definitions Of Civil Engineering Terms
The civil engineering terminology is a ready reckoner that includes the definitions of various technical terms used in the construction industry.
It is important for all the stakeholders to understand the basic terminology used in the construction industry, architecture, and interior design projects.
Civil engineering terminology includes the definition of various building plans and architectural drawings, technical terms, and the terms used for various structural components.

Civil Engineering Terminology
Civil Engineering Teminology
Civil Engineering General Terms Definitions
Building general terms are also used in the construction industry to elaborate on the specific function or purpose of the building component or specifications.
The most commonly used civil engineering general terms include :
Cement
What Is Cement ?

Cement is a binding adhesive material used in the construction industry. Cement is used in the manufacture of cement mortar, concrete, and other cement products. It is also referred to as Ordinary Portland Cement, or OPC.
Cement is manufactured by firing limestone, clay, and other minerals at a high temperature. The binding process of the cement, called hydration, starts only when water is added to the cement.
The cement achieves its full strength after the completion of its hydration process.
Different types of cement are used as per the project needs. The properties of the cement depend on its chemical composition and other physical properties. The heat of hydration is an important criterion for cement.
Curing Of Cement

The term “curing” is the process of maintaining the internal moisture added to cement-based products such as cement mortar and concrete.
The hardening process, called hydration, of cement starts when it is mixed with water. The hardening of cement continues normally for a period of twenty-one days to achieve its full strength.
The curing methods include covering concrete with moist gunny bags, ponding, membrane curing, steam curing, chemical curing and sprinkling water on the cement surface such as plaster or concrete.
Foundation

The term “foundation” in civil engineering is defined as the substructure that is constructed below the ground level on which the superstructure is built.
The foundation transfers the load of the superstructure to the hard underground strata without exceeding the limits of the load-bearing capacity of the soil.
The foundation is designed to support the superstructure built on top of the substructure. Building construction starts with the foundation work.
The foundation types can be broadly categorized into two groups: shallow and deep foundations.
The shallow foundations are column footings, wall footings, and raft foundations. The pile foundation is a type of deep foundation.
Partition Wall

The term “partition wall” in civil engineering is defined as a wall that is designed as a non-load-bearing wall and effectively functions only for the purpose of providing a partition between the two interior spaces.
Partition walls are basically interior walls made-up of any suitable material. These walls are usually of smaller thickness as compared to the main walls.
The main purpose of the partition walls is to functionally divide the two spaces. The decorative walls are also treated as partition walls.
The partition walls are not intended to support any weight of the superstructure other than their own. For example, in the case of the RCC structure, almost all walls are partition walls.
Civil Engineering Terminology
Building Levels
Types Of Building Levels
The building level terminology includes different types of levels defined for various structural components of the building.
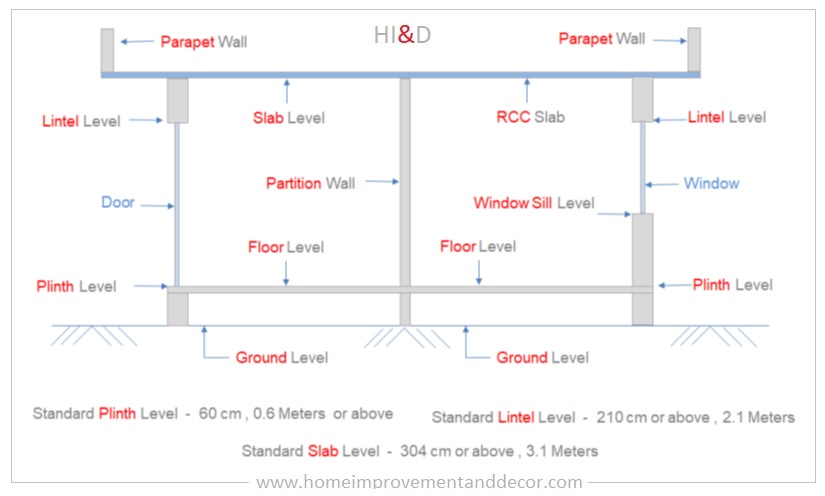
Ground Level
The term “ground level” refers to the average level of the ground around the building. All other levels are either directly or indirectly affected by the ground level. It is also referred to as zero level.
Floor Level
The floor level is considered the same as that of the plinth level. A flooring such as tile, marble, or any other type of floor is constructed on top of the floor level. The term “finished floor level” is used to indicate the top level of flooring material constructed as a floor.
Plinth Level
The plinth level is defined as the top of the foundation, including the damp proof course. The substructure ends at the plinth level, and the superstructure starts at the plinth level. The standard plinth level should be at least 60 cm above the front side road level.
Window Sill Level
The window sill level is defined as the level at which a window frame is installed above the finished floor level. The standard sill level depends upon the size of the window. For example, the French window is installed at floor level.
Lintel Level
The lintel level is defined as the top level of the doors and windows. It is the bottom level of the lintel beam. The standard lintel level should be 2.1 meters for residential buildings and 2.3 meters for commercial buildings.
Slab Level
The slab level is defined as the level at which either an RCC slab or other type of slab is placed or cast. The standard lintel level should be 9.5 feet (2.9 meters) for residential buildings. and 3.35 meters for the commercial buildings.
Civil Engineering Terminology
PCC
What Is PCC ?

PCC stands for plain cement concrete. The concrete is prepared by mixing cement , fine aggregates (sand), coarse ( crushed gravel 20 mm ) and water in the specified proportion.
The PCC is used mainly as a PCC bed during the various foundation beds. The PCC bed can be placed either on the top layer of bolder or on a stabilized strata. The PCC bed can be directly placed and compacted on the stabilized soil.
Plain cement concrete ( PCC ) provides excellent load bearing capacity in terms of its compressive strength. However, plain cement concrete is not considered very good in terms of tensile strength.
The standard ratio ( cement : fine aggregates: coarse aggregates) for PCC mix is ( 1:2:4), used for RCC work. The PCC mix ( 1:3:6 ) is used for the foundation bed to protect the reinforcement.
RCC
What Is RCC ?

The term “RCC” stands for reinforced cement concrete. It is a composite building material made up of concrete and steel reinforcement.
Cement concrete is a versatile construction material extensively used for different types of structural components. The structural components such as column footings, slabs, columns, and beams are required to be designed for both compressive as well as tensile strength.
Plain cement concrete ( PCC ) provides excellent load bearing capacity in terms of its compressive strength. However, plain cement concrete is not considered very good in terms of tensile strength.
In order to improve the tensile strength of the concrete, an additional layer of material is placed inside the concrete to handle the tensile stress. This composite concrete is called reinforced cement concrete ( RCC ).
Civil Engineering Terminology
Scaffolding
What Is Scaffolding ?

The term scaffolding in civil engineering is defined as a temporary structure created on the elevation of the building that works as a platform for the workers to work.
The scaffolding can be erected vertically on any part of the building. The scaffolding serves two purposes.
It provides a stable, protected platform for the worker to comfortably work at high heights. It also provides a platform to keep the tools and building materials during the construction work.
Different types of scaffolding are used in different construction projects. It depends upon the nature of scaffolding requirements and the scale of the project.
Formwork
What Is Formwork ?

The term “formwork” in construction is defined as a temporary mold erected for casting the RCC structural components of the building.
Reinforced cement concrete (RCC) is the most commonly used building material for constructing structural parts such as footings , slabs, columns, and beams.
However, the concrete mix takes considerable time (a minimum of 21 days ) to gain its full strength. During this period, the concrete needs to be cured and cannot be subjected to any loading.
For this reason, a temporary mold of any suitable material (wood, steel , plastic, or composite plates ) is created to cast all the structural components. The steel reinforcement is placed inside the mold as per the structural design.
The reinforcement position is secured by using the cover blocks and the steel chairs. The concrete mix is then poured into this mold.
The concrete mix is compacted with mechanical compactors to remove cavities and air trapped in the concrete mass. This formwork is retained till the time the RCC structure gains its full strength.
The formwork is removed after the specified period is complete. The formwork can be reused for casting other structural members with the same dimensions.
Cantilever
What Is Cantilever ?

The term “cantilever” in civil engineering is defined as a structural member that is embedded into the structure from one end and the other end is protruded to support the overhanging structure of the building.
Common examples of the cantilever include house balcony projections, window canopies, porches, and other such overhanging structures.
The cantilever structural member can either be an RCC beam, a steel beam, a wooden beam or any other suitable material. The cantilever member should be designed for sufficient anchorage and calculated load.
Civil Engineering Terminology
Brick Masonry
What Is Brick Masonry ?

The term “brick masonry” in construction is defined as any construction work built by using bricks and joined together with cement mortar.
The bricks used in the masonry work can be either traditional clay bricks, fly ash bricks, cement blocks, or other types of bricks available on the market.
The most common form of brick masonry work is brick wall construction. The brick wall can be constructed in different thicknesses.
Rubble Masonry
What Is Rubble Masonry ?

The term “rubble masonry” in construction is defined as any construction work built by using different types of stones and joined together with cement mortar.
Rubble masonry can be constructed in two types. In the case of coursed rubble masonry, a design pattern and the course size are maintained throughout the rubble masonry.
Whereas, for uncoursed rubble masonry, the design pattern and the course size are not maintained throughout the rubble masonry. The rubble masonry work is more expensive as compared to the brickwork.
Plumbing System
What Is Plumbing System ?

The plumbing system is an essential component of both residential and commercial projects. The residential projects include home improvement , remodeling, and the construction of new apartments.
The term “plumbing system” in civil engineering is defined as a system of water supply lines, drainage lines, and vent pipes designed for a specific project.
The plumbing system is designed as per the prevailing building code in the respective country.
Drainage System
What Is Drainage System ?

The drainage system is an essential component of both residential and commercial projects. The drainage system is designed to safely dispose of both sewage and sullage waste water.
The term “drainage system” in civil engineering is defined as a system of waste water disposal pipes, manholes, inspection chambers, and vent pipes designed for a specific project.
The drainage system is designed as per the prevailing building code in the respective country.
Wiring System
What Is Wiring System ?
The electrical wiring system is a system designed to provide the electricity supply for a specific project. The electrical wiring system is designed for both residential and commercial projects.
The scope of the wiring system include the selection of type of electrical connection, planning for electrical load calculation, electrical wiring layout and the lighting system.
Civil Engineering Terminology
Grouting
What Is Grouting ?

The grouting in civil engineering is defined as a process of injecting a cement slurry called grout into the cavities and cracks. Some admixtures can be added to the grout to enhance desired properties and effectiveness of the grouting work.
The grouting machines are used for the grouting work. The grout is a mixture of cement, sand, admixtures and water.
Sometimes, cracks and cavities develop into the concrete structures, brick masonry, retaining walls, tunnel lining, hills and rock formation and the soil mass.
These structural cracks can significantly reduce the strength and stability. These cracks are sealed by injecting grout with high pressure grouting machines.
For home improvement projects, the grouting simply means sealing the tile joints with special joint sealant.
Substructure And Superstructure
What Is Substructure ?
What Is Superstructure ?
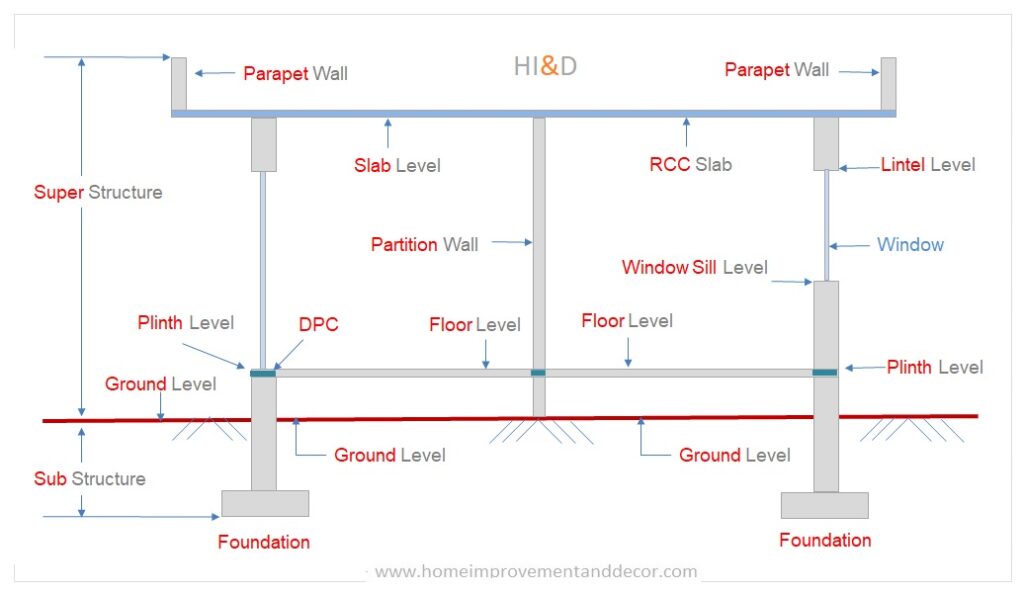
The building construction levels can be broadly split into two levels. The term substructure is referred to the part of the structure that is bellow the ground level.
Whereas, the term superstructure is referred to the part of the building structure above the ground level.
The substructure foundation parts such as column footing, PCC bed and other elements bellow the ground level.
The superstructure includes building parts such as columns, walls, slab and other parts above the ground level.
Civil Engineering Terminology
DPC
What Is Damp Proof Course ?
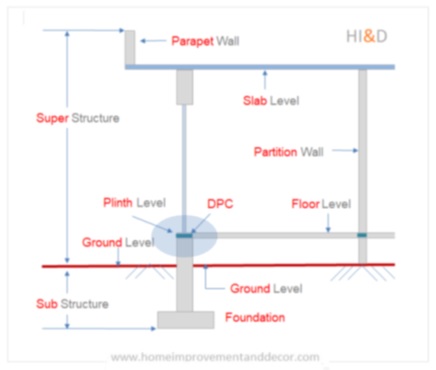
The term DPC stands for damp proof course. The DPC is a layer of waterproof material to prevent the rise of moisture from underground substructure into the superstructure.
The building foundation often comes in contact with the water. This ground water gets absorbed by the substructure parts such as brick masonry. This moisture present in the foundation can find its way to the building superstructure due to capillary action.
This is a major cause of the dampness in the lower portion of the wall. The DPC is a impermeable layer ( usually concrete up to 4 inch thick ) placed at the plinth level between the substructure and superstructure.
The DPC acts as a barrier and protects the superstructure. The DPC prevents the entry of the ground moisture into the building superstructure.
Reinforcement
What Is Reinforcement ?

The term reinforcement in construction is referred to the placement of steel bars into the concrete structures. The composite material of concrete and reinforcement is called RCC that stands for reinforced cement concrete.
The main function of the reinforcement is to improve the tensile strength of the concrete. In RCC structures, the main reinforcement and distribution reinforcement are used.
The combination of different grades of steel reinforcement and concrete are used to achieve the desired strength of the RCC construction.
The reinforcement is designed by the structural engineer for specified design load and technical specifications.
Civil Engineering Terminology
Cement Plaster
What Is Cement Plaster ?

The term cement plaster is a protective coating on the wall with the cement mortar. Most brick masonry work is plastered to render a uniform level surface and to protest the brick work from deterioration. The RCC work and other concrete surfaces such as slab is also plastered to get the required finish.
The plaster functions two important purpose. First, it provides a protective layer on the exposed wall surface and prevents the entry of the moisture. Second, the plaster also provides a level smooth surface and levels out any undulation in the wall surface.
The cement plaster is the most commonly applied plaster. The cement mortar for the plaster work is prepared by mixing cement (OPC), sand ( Fine Aggregates) and water. Depending upon the strength requirements of the cement mortar, the ratio of the cement to sand can be decided.
The standard cement to sand ratio for the preparation of cement mortar for plaster work include ( 1:3 Or 1 : 4 and 1:6 , cement : sand ). The cement plaster work must be cured for recommend period to allow plaster to gain its full strength.